Review of the Leather Industry in Asia: History, Current Status, Challenges, and Future

The leather industry in Asia is one of the fastest-growing and most competitive sectors in the world. Countries like China, India, Vietnam, and Indonesia dominate international markets by producing and exporting both raw leather and finished goods such as footwear, handbags, and clothing. This review explores the history, current status, challenges, and future of the Asian leather industry, highlighting sustainability, technological progress, and economic impact, while also showcasing Asia’s vital role in shaping the global leather trade.
Learn more about leather and make better choices:
1.History of the Leather Industry in Asia:
Ancient and Medieval Periods:
The history of the leather industry in Asia dates back thousands of years. In India, leather was widely used for footwear, garments, and decorative products. In ancient China, leather was essential for making armor and everyday items. These civilizations used simple tanning techniques, but leather was already recognized as a durable and versatile material.
Colonial and Industrial Periods:
During the colonial period, major Asian countries experienced industrial changes that transformed their leather sectors. Many began to treat leather production and exports as vital sources of income. With the introduction of modern machinery and industrial processes from the West, the Asian leather market shifted toward mass production, laying the foundation for the industry’s current global role.

2.Current Status of the Leather Industry in Asia:
Production and Export Leaders:
- China remains the world’s largest producer and exporter of leather and leather goods. Cities like Guangzhou and Shanghai are key hubs for footwear, bags, and apparel manufacturing.
- India is a major player, particularly in the footwear and garment sectors. With its rich animal resources and combination of traditional and modern tanning techniques, Indian cities like Kolkata and Chennai lead in leather exports.
- Vietnam has seen rapid growth in recent years. The country is especially strong in producing leather shoes and handbags. According to recent Vietnam leather goods market trends, cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City are expanding their global reach.
- Indonesia also plays an important role, with regions such as Java and Bali producing high-quality leather for shoes and accessories. The country continues to strengthen its exports to international markets.
Innovations and Technology:
Modernization is reshaping the leather industry in Asia. Countries are investing in advanced tanning techniques, including sustainable leather production in Asia that uses eco-friendly materials and reduces water consumption. China and India, in particular, are pushing for cleaner processes to meet global sustainability standards.
Economic Impact:
The Asian leather industry contributes significantly to local and national economies by creating millions of jobs in production, design, and sales. Exports to Europe, North America, and new developing markets provide a vital source of revenue and strengthen global trade partnerships.
3.Challenges of the Leather Industry in Asia:
Environmental Issues:
One of the most pressing challenges of the leather industry in Asia is its environmental footprint. Traditional tanning processes consume large amounts of water and involve harmful chemicals. Countries like India and China face international pressure to implement greener practices and reduce pollution.
Labor and Legal Issues:
Another concern is labor rights. In some regions, especially within small or traditional workshops, working conditions may be unsafe or unhygienic. Addressing these challenges requires stricter legal frameworks and reforms to protect workers’ welfare.
Global Competition:
Asian producers also face intense competition from countries with lower production costs. Maintaining competitiveness requires a focus on quality, branding, and innovation. The challenges of the leather industry in Asia emphasize the need to adopt modern solutions and respond to global demand effectively.
4.The Future of the Leather Industry in Asia:
Sustainability and Green Tanning:
Emerging economies in Africa, the Middle East, and South America present new opportunities for the leather industry in Asia. By adapting to local preferences and building strong trade networks, Asian producers can increase exports and generate new revenue streams.
Expanding Markets:
Emerging economies in Africa, the Middle East, and South America present new opportunities for the leather industry in Asia. By adapting to local preferences and building strong trade networks, Asian producers can increase exports and generate new revenue streams.
Technological Advances:
The integration of artificial intelligence, automation, and digital design tools is changing the way leather is produced and marketed. These advances allow companies to streamline production, improve product quality, and respond to consumer trends faster. Such technological advances in Asian leather production are expected to reshape the market over the next decade.
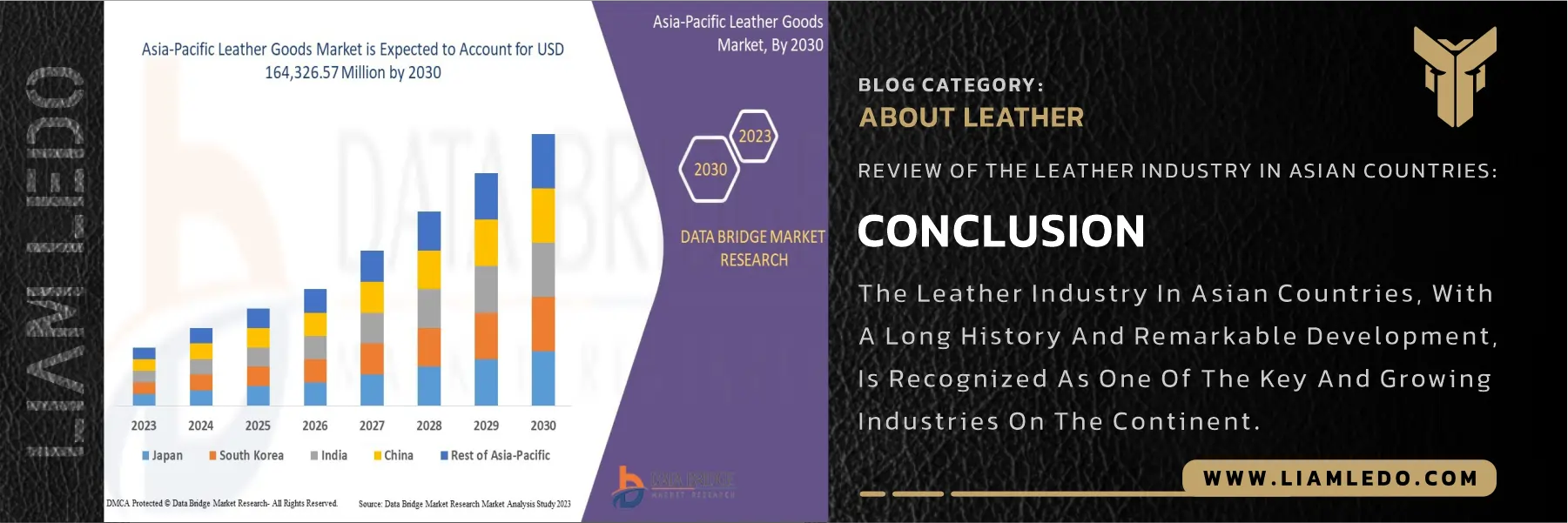
Conclusion:
The leather industry in Asia has a long history and continues to play a vital role in the global economy. From its early roots in China and India to its rapid expansion in Vietnam and Indonesia, the industry has shown resilience and innovation. Despite challenges such as environmental issues, labor rights, and global competition, Asian producers are moving toward sustainability, embracing green technologies, and targeting new markets. Considering these trends, the future of the Asian leather industry looks promising, with opportunities for growth, modernization, and stronger global influence—positioning Asia as a key driver of the industry’s next chapter.
Source: The Gentleman’s Gazette | Wikipedia







